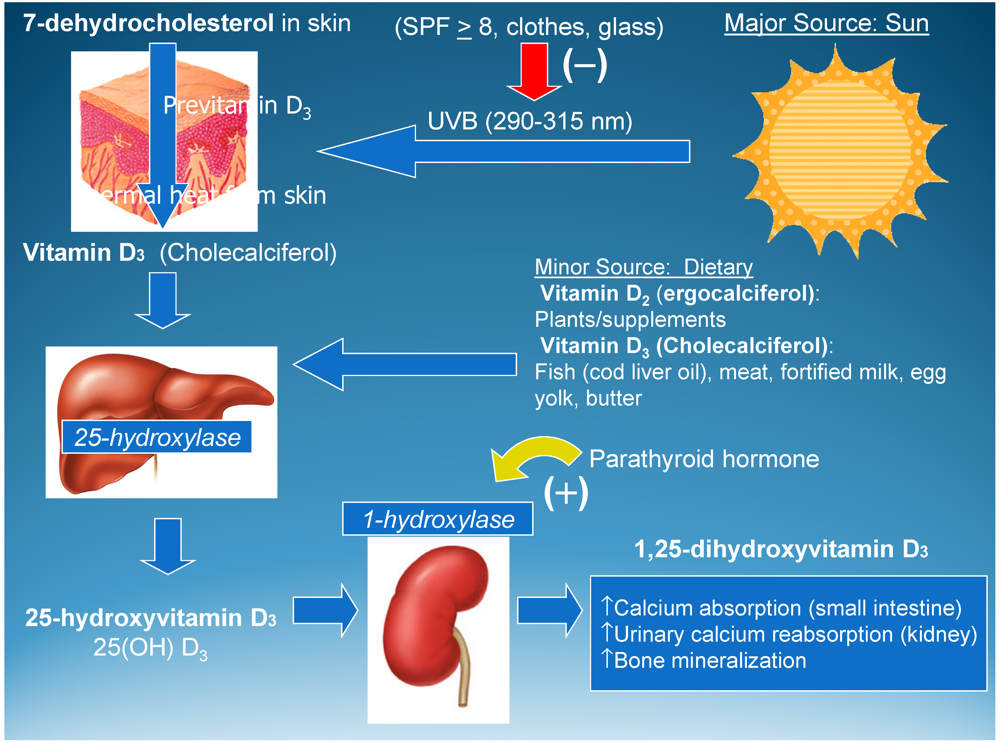
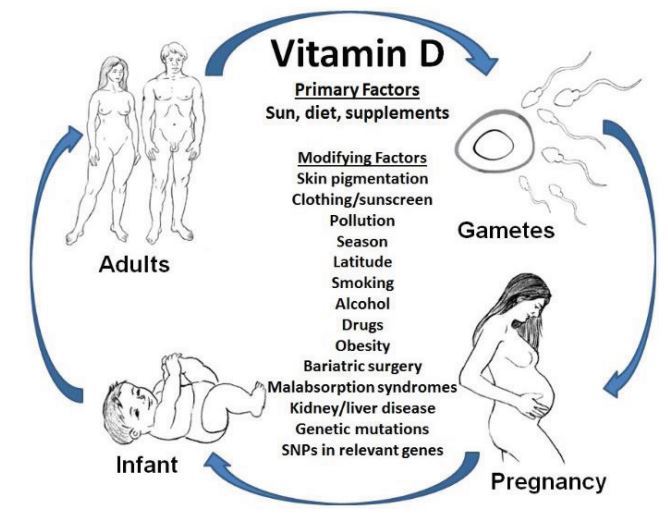
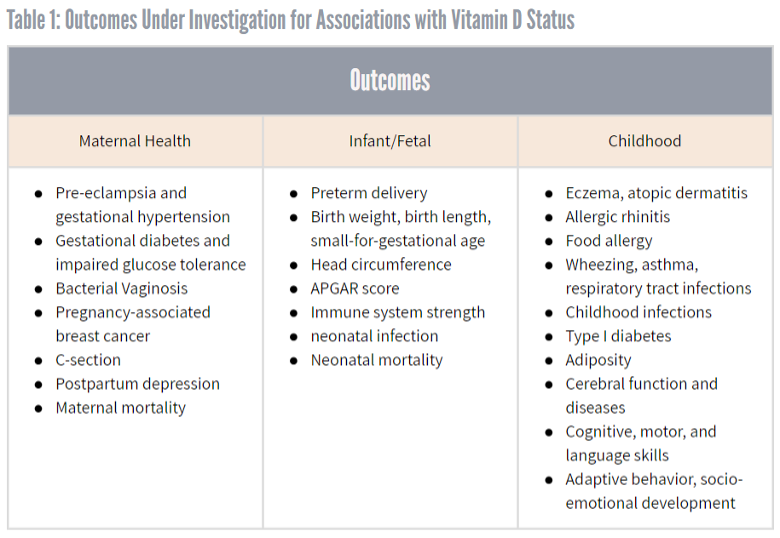
Vitamin D Levels During Pregnancy
Vitamin D Levels During Pregnancy - Low maternal vitamin d concentrations may. Vitamin d deficiency (vdd) in pregnant women and their children is an important health problem with severe consequences for the health of both. Vitamin d deficiency can influence fetal femoral development as early as 19 weeks pregnancy. During pregnancy, vitamin d is transplacentally transferred to the fetus and neonatal levels are reflective of maternal levels.
Low maternal vitamin d concentrations may. During pregnancy, vitamin d is transplacentally transferred to the fetus and neonatal levels are reflective of maternal levels. Vitamin d deficiency (vdd) in pregnant women and their children is an important health problem with severe consequences for the health of both. Vitamin d deficiency can influence fetal femoral development as early as 19 weeks pregnancy.
Vitamin d deficiency can influence fetal femoral development as early as 19 weeks pregnancy. Low maternal vitamin d concentrations may. During pregnancy, vitamin d is transplacentally transferred to the fetus and neonatal levels are reflective of maternal levels. Vitamin d deficiency (vdd) in pregnant women and their children is an important health problem with severe consequences for the health of both.
Maternal Vitamin D Levels During Pregnancy and Their Effects on
Low maternal vitamin d concentrations may. During pregnancy, vitamin d is transplacentally transferred to the fetus and neonatal levels are reflective of maternal levels. Vitamin d deficiency can influence fetal femoral development as early as 19 weeks pregnancy. Vitamin d deficiency (vdd) in pregnant women and their children is an important health problem with severe consequences for the health of.
Are you getting enough Vitamin D, during your pregnancy? Infographics
Vitamin d deficiency (vdd) in pregnant women and their children is an important health problem with severe consequences for the health of both. Vitamin d deficiency can influence fetal femoral development as early as 19 weeks pregnancy. Low maternal vitamin d concentrations may. During pregnancy, vitamin d is transplacentally transferred to the fetus and neonatal levels are reflective of maternal.
Vitamin D During Pregnancy Benefits in Newborn Healthsoul
Vitamin d deficiency (vdd) in pregnant women and their children is an important health problem with severe consequences for the health of both. During pregnancy, vitamin d is transplacentally transferred to the fetus and neonatal levels are reflective of maternal levels. Vitamin d deficiency can influence fetal femoral development as early as 19 weeks pregnancy. Low maternal vitamin d concentrations.
Nutrients Free FullText Vitamin D and Its Role During Pregnancy in
Vitamin d deficiency (vdd) in pregnant women and their children is an important health problem with severe consequences for the health of both. Low maternal vitamin d concentrations may. During pregnancy, vitamin d is transplacentally transferred to the fetus and neonatal levels are reflective of maternal levels. Vitamin d deficiency can influence fetal femoral development as early as 19 weeks.
by Julia
Vitamin d deficiency can influence fetal femoral development as early as 19 weeks pregnancy. During pregnancy, vitamin d is transplacentally transferred to the fetus and neonatal levels are reflective of maternal levels. Low maternal vitamin d concentrations may. Vitamin d deficiency (vdd) in pregnant women and their children is an important health problem with severe consequences for the health of.
Vitamin D levels during pregnancy linked with child IQ
Vitamin d deficiency can influence fetal femoral development as early as 19 weeks pregnancy. Low maternal vitamin d concentrations may. During pregnancy, vitamin d is transplacentally transferred to the fetus and neonatal levels are reflective of maternal levels. Vitamin d deficiency (vdd) in pregnant women and their children is an important health problem with severe consequences for the health of.
Vitamin D During Pregnancy Benefits in Newborn Healthsoul
Vitamin d deficiency can influence fetal femoral development as early as 19 weeks pregnancy. During pregnancy, vitamin d is transplacentally transferred to the fetus and neonatal levels are reflective of maternal levels. Low maternal vitamin d concentrations may. Vitamin d deficiency (vdd) in pregnant women and their children is an important health problem with severe consequences for the health of.
Vitamin D During Pregnancy Importance, Dosage And Foods
Low maternal vitamin d concentrations may. Vitamin d deficiency (vdd) in pregnant women and their children is an important health problem with severe consequences for the health of both. Vitamin d deficiency can influence fetal femoral development as early as 19 weeks pregnancy. During pregnancy, vitamin d is transplacentally transferred to the fetus and neonatal levels are reflective of maternal.
Vitamin D During Pregnancy Why it Matters Well Nourished Mamas
Low maternal vitamin d concentrations may. During pregnancy, vitamin d is transplacentally transferred to the fetus and neonatal levels are reflective of maternal levels. Vitamin d deficiency (vdd) in pregnant women and their children is an important health problem with severe consequences for the health of both. Vitamin d deficiency can influence fetal femoral development as early as 19 weeks.
How Much Vitamin D Do I Really Need During Pregnancy? Nourishing
During pregnancy, vitamin d is transplacentally transferred to the fetus and neonatal levels are reflective of maternal levels. Vitamin d deficiency (vdd) in pregnant women and their children is an important health problem with severe consequences for the health of both. Low maternal vitamin d concentrations may. Vitamin d deficiency can influence fetal femoral development as early as 19 weeks.
Vitamin D Deficiency Can Influence Fetal Femoral Development As Early As 19 Weeks Pregnancy.
Vitamin d deficiency (vdd) in pregnant women and their children is an important health problem with severe consequences for the health of both. Low maternal vitamin d concentrations may. During pregnancy, vitamin d is transplacentally transferred to the fetus and neonatal levels are reflective of maternal levels.